Alcohol is the most commonly abused mood and mind-altering substance in the U.S. More than 85% of adults report drinking at some point in their lifetime and more than half of American adults drink alcohol each month.[1] Although alcohol is involved in many popular American pastimes and is often viewed as a socially acceptable part of life, it is also a toxic and dangerous substance when abused.
Drinking responsibly is extremely important. Excessive drinking can reduce your quality of life, turn into severe alcoholism, and even lead to premature death. Here are 6 ways alcohol and alcoholism can kill you.
1. Alcohol Poisoning/Overdose
You don’t have to be an alcoholic to experience alcohol poisoning–all you have to do is drink too much, too quickly. Alcohol poisoning, also known as alcohol overdose or alcohol toxicity, is a serious and potentially deadly consequence that occurs when people drink too much in a short period of time.
You see, the kidneys and liver can only metabolize alcohol so quickly. In general, a healthy liver can only process one ounce of liquor (one standard drink) per hour. However, many people consume far beyond this amount while drinking. And, if you go too quickly, your liver will become overwhelmed and vital body systems begin shutting down, affecting your heart rate and body temperature.
Symptoms of alcohol poisoning include:
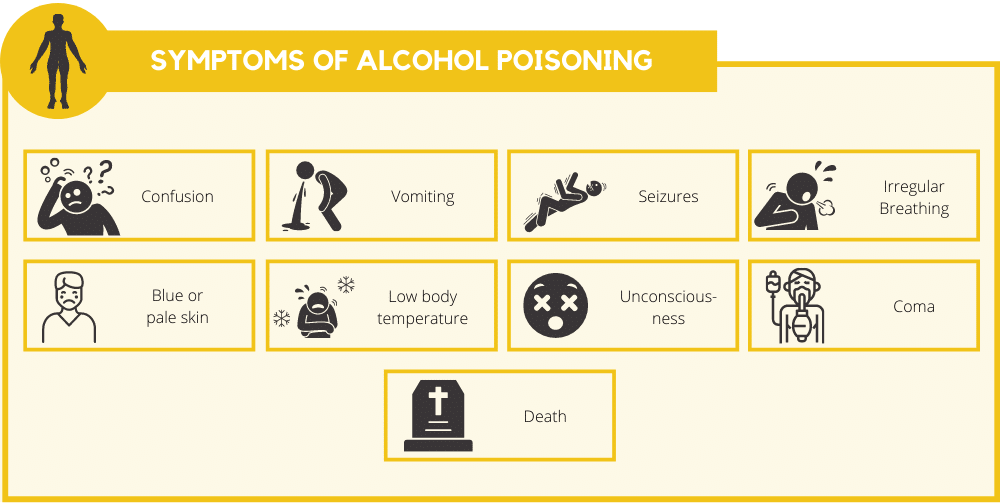
- Confusion
- Vomiting
- Seizures
- Irregular breathing
- Blue or pale skin
- Low body temperature
- Unconsciousness
- Coma
- Death
According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), 6 people die in the U.S. each day, on average, due to alcohol poisoning. Nearly 76% of alcohol poisoning deaths are among men.[2]
2. Drunk Driving
Alcohol impairs your decision-making, coordination, and reaction time, making it extremely dangerous to drive while under the influence. In all 50 states, it is illegal to get behind the wheel of a car and drive if your BAC is over the state’s legal limit. Unfortunately, laws don’t always stop people from doing things they shouldn’t do.
American adults self-report 111 million cases of alcohol-impaired driving each year. While only 1% of these drunk driving cases were arrested for their crime, that doesn’t mean drunk driving isn’t a major problem. Every day, 29 people die in car accidents that involve an alcohol-impaired driver. In 2016, 28% of all traffic-related deaths in the nation involved alcohol.[3]
3. Liver Disease

Alcohol-related liver disease (ALRD) doesn’t often occur in casual or moderate drinkers, however, it is one of the most common ways the disease of alcoholism can kill you. After all, the liver does most of the work when it comes to metabolizing alcohol, so it takes a major toll after years of excessive drinking.
The three most common types of liver disease that are common causes of death among alcoholics are:
- Fatty liver disease – Occurs as a result of fat build-up around the liver and is often asymptomatic. Without detection, it can lead to more severe types of liver disease.
- Alcoholic hepatitis – Also known as liver inflammation and is a progressively fatal disease when left untreated. Early symptoms include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach pain, and jaundice.
- Cirrhosis – This is the most serious and life-threatening alcohol-related liver disease. It occurs when normal liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue. This scar tissue is not reversible so the condition is often fatal.
From 2010-2016, ALRD was responsible for one-third of needed liver transplants in the United States. Additionally, in 2019, approximately 36,845 individuals died as a result of alcohol-related liver disease.[1]
4. Certain Types of Cancer
Chronic drinking, usually drinking that lasts 10 or more years, can increase your risk of developing an array of deadly cancers. Some types of cancer associated with alcohol use that can kill you include:
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Stomach
- Colon
- Rectum
- Mouth
- Throat
- Voicebox
- Esophagus
- Breast* – The American Cancer Society notes consuming even small amounts of alcohol can increase the risk of breast cancer.[4]
While people are still diagnosed with these types of cancer without alcohol being a contributing factor, alcoholism significantly increases cancer risk.
5. Heart Disease/Heart Failure
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Unfortunately, excessive alcohol consumption and alcoholism increase the probability of dying from heart conditions. This is primarily because drinking is linked to high blood pressure and obesity, both of which contribute to heart conditions. However, drinking also increases the level of triglycerides (harmful fats) in the blood. This can result in high blood pressure, increased caloric intake, and heart failure.
In the long term, the development of heart disease as a result of alcoholism can lead to stroke, sudden cardiac death, and cardiomyopathy.[5]
6. End-Stage Alcoholism
There are a number of other ways alcoholism can kill you that don’t fit into any single category. There are four stages of alcoholism, with the last and most severe being end-stage alcoholism. At this stage, the body begins deteriorating. Cells lose the ability to regenerate or health themselves, the liver struggles to supply essential nutrients to the rest of the body, and complications can occur in the central nervous system. Individuals in end-stage alcoholism become more susceptible to severe illnesses like pneumonia, bronchitis, and other life-threatening conditions.
Find Help for Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Today
If you struggle to control or moderate your drinking, you may be struggling with alcoholism. The longer you abuse alcohol and delay getting treatment, the more your body is impacted by the devastating health impacts of alcohol addiction. And, whether you like it or not, alcohol and alcoholism can kill you.
Here at Daylight Recovery Center, we want to help you stop drinking, improve your health, and live the life you were meant to live. Beginning with detox and ending with discharge planning, our team will be by your side. Don’t wait any longer. Give us a call now to get started.
References:
- niaaa.nih.gov
- https://www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/alcohol-poisoning-deaths/index.html
- cdc.gov
- cancer.org



